Explore the essentials of electoral vote counting, including legal frameworks, input requirements, phases, and the impact on election outcomes.In the realm of democratic processes, the counting of electoral votes plays a pivotal role in shaping the outcomes of elections. Understanding The Process Of Electoral Vote Counting demystifies this crucial procedure, shedding light on the intricate steps involved. From grasping the foundational elements of vote counting to addressing legal frameworks that govern the process, this article provides a comprehensive overview. We will delve into the essential input requirements for electors, explore the various development phases of the counting process, and examine the significant impact that accurate vote counting has on overall electoral integrity. Whether you’re a curious citizen or an aspiring electoral expert, this guide aims to clarify the complexities of vote counting and its importance in safeguarding democratic principles. Join us as we navigate through the essential components of this vital civic duty.
Understanding The Basics Of Electoral Vote Counting
In the intricate realm of electoral processes, Understanding The electoral vote counting procedure is paramount. The electoral vote counting method is a systematic approach employed to ensure that every vote is accounted for and appropriately tallied to reflect the will of the electorate.
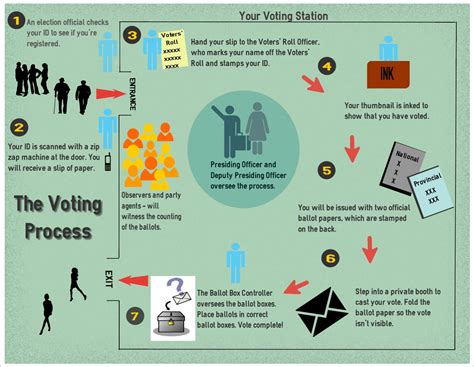
This process begins with the collection of votes cast during elections, which may include ballots submitted in person, by mail, or via electronic means. These votes are then aggregated within each state to determine the total count for each candidate. The crucial aspect here is that each state has its own methodology and timeline when it comes to counting and reporting the results, reflecting the decentralized nature of the electoral system in places like the United States.
The mechanics of counting electoral votes can be broken down into several key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Ballot Collection | Gathering all forms of ballots from various voting methods utilized by the electorate. |
| Tabulation | Using machines or manual processes to tally votes accurately. |
| Verification | Ensuring the integrity of the counted votes through audits or recounts as necessary. |
| Certification | Officially confirming the results and reporting them to the relevant authorities. |
Throughout this process, transparency and accuracy are emphasized to protect the integrity of the electoral system. Observers, including representatives from each party, often monitor the counting process to foster trust and ensure that any discrepancies are promptly addressed.
Overall, a solid grasp of the Understanding The fundamental aspects of electoral vote counting is essential for comprehending how democratic processes function and for ensuring that the voices of the electorate are faithfully represented in election outcomes.
Input Requirements For Electors In The Vote Counting Process
In the realm of electoral vote counting, there are specific input requirements that electors must meet to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the election process. Understanding the intricacies of these requirements is crucial for both electors and voters.
Electors typically need to provide the following:
By fulfilling these input requirements, electors contribute to the smooth functioning of the electoral vote counting process, thereby reinforcing the democratic framework of the electoral system. Understanding the requirements helps to enhance transparency and builds public trust in the overall election outcome.
Development Phases Of Electoral Vote Counting Explained
The process of electoral vote counting involves several critical phases that ensure the accuracy and integrity of the electoral outcome. Each phase is designed to meticulously handle the votes from initial casting to final certification. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each stage involved:
- Preparation: This is the initial phase where election officials set up the necessary infrastructure for counting votes. This includes training workers, ensuring that counting equipment is operational, and conducting pre-election tests to verify that the systems are functioning correctly.
- Receiving Ballots: Once the polls close, the next step is to collect all the ballots from various polling places. This phase requires strict adherence to security protocols to prevent tampering. Absentee and mail-in ballots are also gathered during this time.
- Ballot Verification: Before counting begins, election officials check the collected ballots for validity. This can involve verifying signatures on mail-in ballots and ensuring that no duplicate votes are counted. This phase is critical for maintaining voter integrity and confidence in the system.
- Counting Votes: The actual counting of votes occurs in this phase. Depending on the jurisdiction, this can be done manually or through electronic counting machines. This process is closely monitored by representatives from different political parties to ensure transparency.
- Quality Control: After the initial count, a quality control phase is performed. This includes auditing a sample of the ballots to confirm the accuracy of the counting process. If discrepancies arise, further investigation may be undertaken to ensure the correct final tally.
- Certification of Results: Once all votes have been counted and verified, the election results are certified by the appropriate election authority. This phase includes officially documenting the results and addressing any legal challenges that may arise.
- Reporting: The final phase involves publicly reporting the results. This phase is vital for public transparency and communication. The results are disseminated through various channels, including official websites, media outlets, and press conferences.
Understanding The phases of electoral vote counting is essential for grasping how democratic elections function and ensuring that the electoral process remains secure and reliable. Each stage plays a vital role in upholding the integrity of elections, which ultimately reflects the will of the voters.
Understanding The Legal Framework Governing Vote Counting
When it comes to Understanding The legal framework surrounding electoral vote counting, it’s essential to recognize the combination of federal, state, and local laws that regulate this process. Each state in the U.S. has its own set of rules that govern how votes are counted, reported, and certified. Understanding these laws is crucial for ensuring that the vote counting process is transparent, accurate, and fair.
The U.S. Constitution outlines the foundational elements of the electoral process, including the delegation of power to states to administer elections. Article II, Section 1 specifies that each state appoints electors in a manner of its choosing, which encompasses how votes are counted and reported. Additionally, the Voting Rights Act of 1965 plays a significant role in protecting the voting rights of citizens and ensuring compliance with federal election laws.
State election laws detail the specific procedures for counting votes, including the use of electronic voting machines, paper ballots, and mail-in voting. These laws also outline the standards for what constitutes a valid vote, the time frames for counting and reporting results, and the processes for handling disputes. For instance, some states require a public audit of election results to ensure accuracy and build public trust.
The role of election officials cannot be overstated. They are tasked with implementing these laws, overseeing the vote counting process, and ensuring all procedures are followed. Their actions are often subject to scrutiny, which underlines the importance of transparency in the electoral vote counting process.
Moreover, in the event of legal challenges or discrepancies in the vote counting process, courts may become involved. Judiciary rulings can significantly impact the outcome of elections by interpreting laws or resolving disputes that arise during the counting process. Such cases highlight the intricate relationship between the electoral process and the legal framework designed to uphold it.
Understanding The legal framework governing vote counting is integral to appreciating the complexities of electoral processes. It ensures that elections are conducted fairly, accurately, and transparently, thus maintaining the integrity of the democratic process.
Resulting Impact Of Electoral Vote Counting On Elections
The process of electoral vote counting plays a crucial role in shaping the outcome of elections, influencing not only the immediate results but also the broader political landscape. Understanding the impact of this process helps citizens grasp why every vote counts and how these votes are transformed into tangible outcomes in a democracy.
One of the most significant impacts is seen in the electoral transparency and integrity. The manner in which votes are counted and reported can either bolster public trust in the electoral process or lead to widespread skepticism. Accurate and transparent counting can enhance voter confidence, encouraging higher participation in future elections.
Moreover, the results of electoral vote counting can have substantial political ramifications. A closely contested election, where the counting process is drawn out or contentious, can lead to political instability or even unrest. Consequently, the way votes are counted not only affects the current election cycle but can also influence future electoral strategies from political parties and candidates.
Political narratives are often shaped by the outcomes of electoral vote counting. For instance, a candidate’s potential to win can be dashed or fortified by the timely reporting of results. Thus, these dynamics can affect policy discussions, party alignments, and voter engagement strategies.
Additionally, the implications of electoral vote counting extend to advocacy and reform movements. If the public perceives the counting process as flawed, it may lead to calls for changes in legislation or reforms in the electoral system. Such shifts can redefine how elections are conducted and how votes are counted in the future.
The impact of electoral vote counting on elections is profound. It influences public trust, political stability, candidate narratives, and potential reforms—thus highlighting the importance of understanding the intricate processes involved in turning individual votes into definitive election outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is electoral vote counting?
Electoral vote counting is the process by which the votes cast by electors in the Electoral College are tallied to determine the outcome of a presidential election.
Why is the electoral vote important?
The electoral vote is crucial as it officially determines the winner of the U.S. presidential election, reflecting the will of the voters in each state.
How does the Electoral College work?
The Electoral College consists of 538 electors, with each state having a set number of electors based on its population. To win the presidency, a candidate must receive a majority of the electoral votes, which is at least 270.
What happens on the night of the election regarding electoral votes?
On election night, states close their polls, and preliminary results start coming in, which indicate how many votes each candidate received. However, official counting of electoral votes occurs later.
Are electoral votes counted on the same day in all states?
Yes, electoral votes are counted on the same day across all states, specifically on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November, in accordance with federal law.
What is the role of Congress in electoral vote counting?
Congress plays a significant role in the counting of electoral votes. A joint session of Congress is held in January, where the electoral votes are officially counted and results are confirmed.
What can happen if there are challenges to the electoral vote count?
If there are challenges during the counting process, Congress must address these objections. A majority vote is required in both the House and Senate to uphold or dismiss any challenge.