Explore the significance, methodology, and future of election polls, their impact on voter behavior, and key trends influencing outcomes in this insightful blog post.As election season heats up, understanding the intricacies of election polls becomes essential for both voters and political enthusiasts. Election Polls Today: What The Numbers Are Saying offers an insightful exploration into how these polls are conducted, their influence on voter behavior, and the latest trends shaping the current political landscape. From the art of polling methodology to the unpredictable nature of voter sentiment, we delve into the numbers and their implications for upcoming elections. Discover how accurately we can predict outcomes and what innovations and challenges lie ahead in this dynamic field. With our comprehensive analysis, you’ll gain a clearer picture of the electoral process and make more informed decisions as you engage with the democratic system. Join us on this journey to unravel the mysteries behind the numbers that shape our elections.
Understanding Election Polls: How They Are Conducted
Election polls are essential tools used to gauge public opinion during an election cycle. Understanding how these polls are conducted is crucial to interpreting their results accurately. Here’s an overview of the fundamental steps involved in the process of conducting election polls.
1. Defining the Target Population
The first step in any election polls process is to clearly define the target population. This typically includes registered voters likely to participate in the upcoming election. Pollsters must ensure that the sample accurately reflects the demographics of the voting population, including age, gender, race, and geographical distribution.
2. Sampling Methodology
Once the target population is defined, pollsters decide on a sampling methodology. Two common methods are:
- Random Sampling: Participants are chosen randomly from the population, giving each individual an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified Sampling: The population is divided into subgroups (strata), and samples are drawn from each stratum proportionally to its size within the overall population.
3. Questionnaire Design
The next step involves crafting the questionnaire. Questions must be clear, unbiased, and designed to elicit genuine responses. Multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and Likert scales are common formats. Questions often cover voters’ preferences, issues of importance, and party affiliation.
4. Data Collection
Data collection can occur through various methods, including phone interviews, face-to-face surveys, or online questionnaires. Each method has its pros and cons, influencing the response rate and the type of demographic data collected.
5. Data Analysis
After collecting the responses, data analysts interpret the findings. This step involves coding the responses, running statistical analyses, and checking for biases or anomalies. Polling firms often weight the results to ensure the findings reflect the population accurately.
6. Reporting Results
The results of the election polls are compiled into reports and disseminated to the public. It is crucial for these reports to include methodological details so that consumers of the data can gauge its reliability and validity.
Understanding the methodology behind election polls helps voters and political analysts alike discern the narratives these numbers create and their implications for the election cycle.
The Impact of Election Polls on Voter Behavior
Election polls play a significant role in shaping voter behaviors and perceptions. These polls can influence voters in several ways:
- Perception of Viability: When polls show a candidate leading, it can create a perception of their viability as a contender. Voters may gravitate towards candidates they believe can win, a phenomenon known as bandwagon effect. This can amplify support for the frontrunner while diminishing enthusiasm for those trailing.
- Disenfranchisement: Conversely, if a candidate is consistently polling low, their supporters might feel discouraged, leading to reduced voter turnout. The fear of wasting a vote can deter individuals from participating in the electoral process.
- Informed Decision-Making: Polls can also serve as a source of information, helping voters understand key issues, candidate positions, and public sentiment. However, relying solely on these numbers may oversimplify complex electoral dynamics.
- Strategic Voting: Voters may choose to support a candidate they perceive as having a better chance of winning against a less desirable opponent, primarily if polls indicate a close race. This strategic voting can undermine the plurality of choice among candidates.
- Feedback Mechanism: Candidates often adjust their strategies based on polling results to better align with voter preferences. Thus, polls can serve as a feedback mechanism to mold campaign messaging and focus areas.
election polls undoubtedly impact voter behavior, shaping perceptions of candidates and altering the electoral landscape. Understanding these effects can provide deeper insights into how elections unfold.
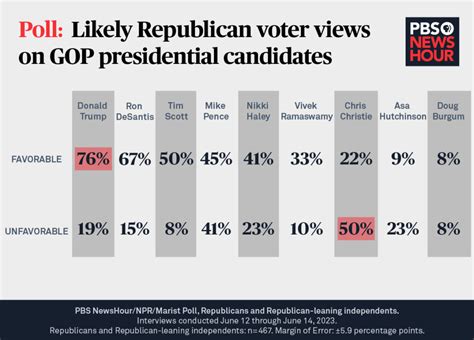
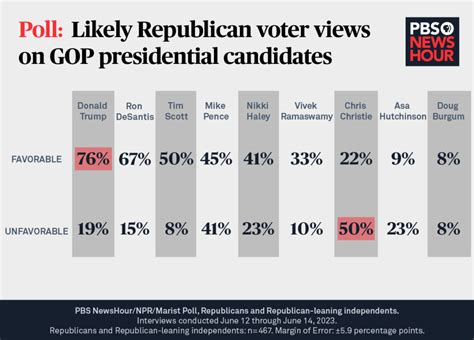
Analyzing Current Election Polls: Key Trends and Insights
As we delve into the latest trends emerging from Election Polls, it’s crucial to recognize how they reflect the dynamic political landscape. Analyzing current polls gives us a snapshot of public sentiment, revealing critical insights into voters’ preferences and the overall electoral climate.
One key trend in recent Election Polls is the increasing influence of social media on public opinion. Many voters are now turning to platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and TikTok for their information, which can both positively and negatively skew polling results. These platforms often amplify extreme opinions, causing traditional polling methods to struggle in accurately reflecting the electorate’s true sentiments.
Moreover, demographic shifts are playing a significant role in shaping Election Polls. The younger generation, particularly first-time voters, shows distinct preferences compared to older voters. This change could lead to unexpected outcomes if their participation rates surpass those of previous elections.
Another interesting observation is the impact of major events, such as economic fluctuations or social movements, on polling data. For instance, recent polls indicate fluctuating support for candidates in response to specific policy proposals or social issues gaining traction. Analyzing these shifts helps predict how candidates might adapt their strategies as they respond to voter concerns.
It is essential to consider the methodology of Election Polls. The techniques and sampling methods used can significantly influence the outcomes. Polls incorporating weighted samples to better reflect voter demographics often yield more accurate results. Therefore, examining the methodology behind the data gives us deeper insights into the reliability of the polls.
Analyzing current Election Polls allows us to understand key trends that could influence the upcoming elections. By staying informed about these trends, both voters and candidates can make more strategic decisions and engage more thoughtfully in the electoral process.
Election Polls Explained: Predicting Outcomes and Their Accuracy
Election polls are vital tools used to gauge public opinion and forecast electoral outcomes. These polls gather information from a sample of the population to predict how the broader electorate is likely to vote. However, the accuracy of these predictions can vary widely based on several factors.
One of the main methodologies for conducting election polls is through random sampling, where pollsters select individuals at random to participate. This approach aims to create a microcosm of the voting population, ensuring a diverse representation in the data. However, obtaining a truly representative sample can be challenging, especially in a rapidly changing political landscape.
Weighting is another crucial aspect of election polls. Pollsters often adjust their results to account for demographic differences such as age, race, and gender. While this process can enhance accuracy, it also introduces a potential for bias if the weights applied are not reflective of the actual voting population.
Moreover, the timing of a poll can significantly influence its accuracy. Public opinion can shift rapidly in response to news events, debates, or campaign strategies, making polls conducted well ahead of an election potentially misleading. Daily tracking polls can offer a more current snapshot, but they come with their own set of challenges regarding sample size and methodology.
We must consider the margin of error inherent in any statistical survey. Most election polls will provide a margin of error, indicating the range within which the true values lie. A small margin of error suggests greater precision, but it’s essential for consumers of this data to understand that these figures are only estimates and should be interpreted with caution.
While election polls provide invaluable insights into voter preferences and potential election outcomes, their accuracy is influenced by sampling methods, weighting adjustments, timing, and inherent margins of error. As technology and methodologies evolve, the quest for more accurate predictions continues, illuminating the complexities of public sentiment in the electoral process.
The Future of Election Polls: Innovations and Challenges Ahead
As technology continues to evolve, the future of Election Polls is poised for significant transformation. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and social media monitoring are already beginning to reshape how polls are conducted and interpreted. These advancements offer opportunities to gather more nuanced insights into voter preferences and behaviors, potentially leading to more accurate predictions.
One major innovation is the integration of machine learning algorithms, which can analyze complex data sets and identify emerging trends in real-time. This not only enhances the accuracy of Election Polls but also allows pollsters to refine their methodologies continuously based on practical feedback from previous elections.
However, with these innovations come several challenges. One prominent issue is the increasing skepticism around polling accuracy, sparked by previous high-profile election outcomes that deviated significantly from poll predictions. This has led to calls for greater transparency in polling methodologies and the need for pollsters to communicate the margins of error clearly to the public.
Additionally, the rise of social media as both an informational platform and a polling tool presents its own set of challenges. The potential for misinformation and echo chambers can skew public perception and the data collected from these platforms. Ensuring that Election Polls are not only representative but also shielded from these pitfalls is crucial for maintaining their credibility.
Moreover, the decline in traditional landline usage impacts the way polls are conducted, as a significant portion of the population can now be difficult to reach through conventional means. This shift necessitates the development of new strategies in polling, such as more targeted online surveys and outreach through mobile applications.
While the future of Election Polls is filled with exciting innovations that could improve forecasting accuracy, pollsters must also navigate the complexities of public trust, data integrity, and changing communication channels. Balancing innovation with reliability will be key as we move forward in an increasingly dynamic political landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are election polls and why are they important?
Election polls are surveys that measure public opinion on political candidates and issues. They are important because they provide insights into voter preferences and behavior, helping campaigns strategize effectively.
How are election polls conducted?
Election polls are typically conducted through various methods such as telephone interviews, online surveys, or in-person polling. Pollsters aim to gather a representative sample of the population to ensure accurate results.
What do the latest election polls suggest about voter sentiment?
The latest election polls indicate a shift in voter sentiment towards certain candidates or parties, highlighting key issues that resonate with the electorate. These insights can vary widely based on demographics and geography.
What factors can influence the accuracy of election polls?
Factors influencing the accuracy of election polls include sample size, demographic representation, timing of the poll, the phrasing of questions, and the methodology used in data collection.
How can readers interpret conflicting election poll results?
Readers should consider the source of the polls, sample size, and methodology when interpreting conflicting results. It’s also important to look at trends over time rather than relying on a single poll.
What role does margin of error play in election polls?
The margin of error indicates the potential range of error in poll results, reflecting the uncertainty inherent in sampling. A smaller margin suggests higher confidence in the accuracy of the poll.
Why should voters pay attention to election polls ahead of voting day?
Voters should pay attention to election polls as they can provide insights into how their preferred candidates might perform, the critical issues that are influencing voters, and potential electoral outcomes that may affect policy.