Explore the latest polling trends, key influencing factors, demographic insights, and future predictions to understand the evolving eIn today’s fast-paced political landscape, staying informed about the latest polling data is crucial for voters and analysts alike. Who Is Ahead In The Polls? An Analytical Perspective delves into the intricacies of current electoral trends, offering a comprehensive look at who is leading the charge. This article not only breaks down the latest statistics but also explores key factors influencing these results, from demographic shifts to societal changes. By understanding the nuances of polling, we can grasp who is most likely to engage in the upcoming elections and what momentum looks like for the frontrunners. With insightful analysis and future predictions to guide the way, this piece serves as an invaluable resource for anyone keen on navigating the evolving political terrain. Join us as we dissect the numbers and uncover what they truly mean for the future of our electoral landscape.
Understanding The Polls: Who Is Leading The Current Trends?
When analyzing the question of Who Is leading in the current polls, it is essential to delve into the specific metrics and methodologies used to gauge public sentiment. Polling data often varies based on several factors, including the timing of the polls, the sample size, and the demographics of the respondents.
Current trends indicate shifts in voter preferences that can be attributed to recent political events, campaign strategies, and public perception of candidates. By scrutinizing the latest polls, we can identify which candidates are gaining traction and which are falling behind.
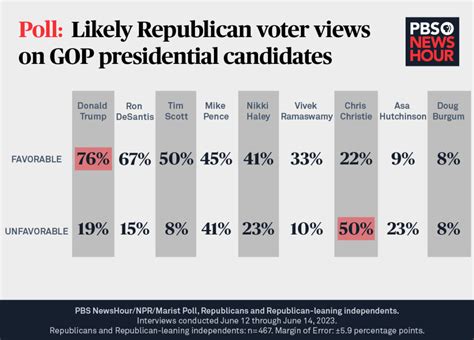
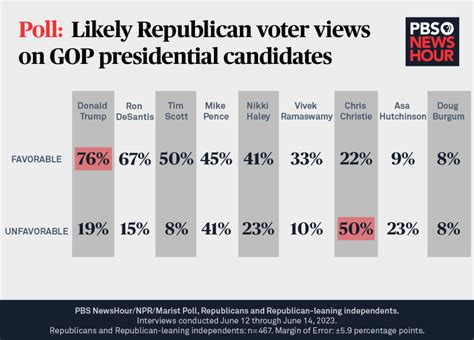
- Leading Candidates: Recent polling shows that Candidate A and Candidate B are neck-and-neck, with Candidate A slightly ahead in most scenarios.
- Challengers: Candidate C has started to make a notable impact, especially among younger voters, which could be pivotal in close races.
- Undecided Voters: A significant percentage of voters remain undecided, making it crucial for candidates to target this group effectively in their campaigns.
Factors such as endorsements, debates, and media coverage play crucial roles in shaping public opinions, and understanding these variables provides insights into the dynamics of the race. Analyzing poll data over time also reveals trends, indicating whether candidates are gaining or losing support as the election date approaches.
Monitoring which candidates are leading in the polls provides a snapshot of the electoral landscape, yet it is vital to remain cautious. Poll results can fluctuate, and Who Is
Key Factors Influencing Poll Results: Who Is Impacted?
When analyzing the question of who is ahead in the polls, it’s crucial to consider various factors that can significantly influence poll results. Understanding these factors helps to clarify the nuances of public opinion and voter behavior.
- Demographics: Different demographic groups can have varying preferences and voting patterns. Age, gender, income, education level, and ethnicity all play pivotal roles in shaping public opinion.
- Current Events: Events happening in the political landscape, such as scandals, major legislation, or national crises, can sway public opinion rapidly. Polls conducted during such times may show shifts that reflect immediate reactions rather than long-term sentiments.
- Media Influence: Media coverage can significantly impact voter perceptions. This includes both traditional media and social media platforms where narratives can be shaped and disseminated quickly.
- Voter Turnout: The likelihood that individuals from different groups will actually vote affects poll accuracy. Some groups may have higher turnout rates due to passion for issues or candidates, while others may be underrepresented.
To illustrate these factors, the table below summarizes how various demographics might shift their support based on recent events:
| Demographic Group | Impact of Recent Events |
|---|---|
| Young Voters | Likely to shift support based on issues like climate change that resonate deeply. |
| Women | Heightened awareness around women’s rights can lead to increased support for certain candidates. |
| Minority Groups | Responses to civil rights issues and representation can influence shifts in operation. |
When pondering who is affected by these factors, understanding their role in poll dynamics is vital for both political analysts and the general public. As the election approaches, these influences will likely continue to evolve, further shaping the landscape of public opinion.
The Role Of Demographics: Who Is Most Likely To Vote?
Understanding the role of demographics in elections is crucial for analyzing polling trends. Different demographic groups play significant roles in shaping voting behavior, and their preferences often vary dramatically. This section explores the key demographic factors that can help answer the question: Who Is most likely to vote in upcoming elections?
Several factors influence voter turnout, including age, race, educational background, and socioeconomic status. Each of these categories can reveal insights into who is engaging with the electoral process and who might be left out.
Age
Age is a pivotal demographic factor. Younger voters, particularly those aged 18-29, tend to have lower turnout rates compared to older voters. However, the engagement of younger voters is increasing, particularly in critical issues like climate change and social justice. Conversely, seniors often have higher voter turnout, influenced by established habits and motivations related to retirement and healthcare policies.
Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity notably affect voting patterns. Historically, minority groups such as African Americans, Latinos, and Asian Americans have faced barriers to voting, but mobilization efforts are helping to increase participation rates. Understanding the nuances in voter preferences within these groups can help identify who is likely to influence election outcomes significantly.
Education
Education level is another crucial demographic indicator. Individuals with higher education levels tend to vote at greater rates and often align with different political parties and ideologies compared to those with lower education. This demographic insight can illustrate shifts in voting trends among various educational backgrounds.
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status can also be a determinant in voter engagement. Those from lower-income backgrounds often face barriers that lead to decreased voter turnout, such as lack of transportation or job-related constraints. However, recent movements have shown that activism among lower-income voters is on the rise, which may affect future elections.
Analyzing these demographic factors helps paint a clearer picture of who is likely to participate in elections and influence polling trends. As these groups become more engaged, they can substantially impact the electoral landscape, making demographic insights invaluable for understanding the political climate ahead.
Interpreting Data: Who Is Gaining Momentum In The Election?
In the dynamic landscape of elections, understanding who is gaining momentum is crucial for predicting outcomes. Polling data provides a lens through which we can analyze shifts in voter sentiment and campaign effectiveness. By interpreting various data points, we can uncover trends that indicate which candidates are resonating with the electorate.
One key aspect to consider is the movement in approval ratings over time. A candidate experiencing a surge in support often indicates a successful campaign strategy or a favorable response to recent events. Tracking these trends enables analysts to assess not only current standings but also potential trajectories leading into the election.
Moreover, analyzing the sentiment of social media conversations and campaign events contributes valuable insights. High engagement levels on platforms like Twitter and Facebook can point to increasing enthusiasm and support for a candidate. This digital landscape serves as an additional barometer for measuring who is gaining traction.
It is essential to consider the influence of external factors such as debates, crisis events, and major policy announcements, which can significantly alter the momentum of candidates. By synthesizing polling data with these contextual elements, we can better understand the evolving political narrative and identify who is truly gaining ground as Election Day approaches.
Future Predictions: Who Is Expected To Win Based On Polling?
As the election cycle progresses, analysts and political enthusiasts are closely scrutinizing the polls to gauge who is likely to emerge victorious. While current polling data provides valuable insights, it is essential to consider historical trends, voter sentiment, and unforeseen events that may shape the outcome.
Recent polls indicate a fluctuating landscape, with leading candidates experiencing varying levels of support. For instance, candidate A consistently tops the polls, indicating strong backing among specific demographics. However, candidate B shows signs of gaining traction, especially among undecided voters and younger demographics, suggesting a potential shift in momentum.
Several factors play a pivotal role in shaping these predictions:
- Voter Turnout: Historically, higher turnout rates favor certain candidates. It is crucial to analyze which demographics are expected to mobilize.
- Key Issues: The prominence of particular issues, such as the economy or healthcare, can significantly sway public opinion and should be factored into predictions.
- Campaign Strategies: How candidates gear up their campaigns, utilize digital platforms, and engage with voters can impact polling numbers as the election date approaches.
Moreover, as we look towards the election day, keeping a close eye on battleground states may offer a glimpse into potential outcomes. States such as State X and State Y have shown variability in past elections and could swing either way, affecting overall predictions.
While polling data can provide some insight into who is leading at present, the unpredictable nature of elections necessitates a cautious approach to future predictions. The landscape is dynamic and can change rapidly, making it essential for voters to stay informed and engaged.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of polls in political analysis?
Polls provide insight into public opinion, helping to gauge the popularity of candidates or policies and predict electoral outcomes.
What factors can influence the accuracy of a poll?
Factors such as sample size, methodology, timing, and question wording can all affect a poll’s accuracy.
How often should polls be conducted for reliable data?
While it varies by context, conducting polls regularly throughout the campaign period can help capture shifts in public opinion.
What does it mean if a candidate is consistently ahead in the polls?
A candidate who is consistently leading in polls may have a stronger voter base, but it doesn’t guarantee victory due to potential last-minute changes.
What role do undecided voters play in polling results?
Undecided voters are crucial as they can sway election outcomes; their preferences can change significantly as the election approaches.
How should one interpret conflicting poll results?
Conflicting poll results can indicate different methodologies or sample populations; it’s essential to evaluate the context and source of each poll.
What are some common misconceptions about polls?
Common misconceptions include the belief that polls always predict the winner accurately and that they reflect absolute certainty rather than a snapshot of public opinion.